快速上手,五分钟内完成个性化Python GUI计算器搭建
创始人
2025-07-10 11:00:59
0次
一、前言
在本教程中,你将学习如何在Python中使用Tkinter在短短几分钟内制作自己的全功能GUI计算器。
在完成本教程时,除了通常随Python标准库一起安装的Tkinter之外,不需要任何额外的库。
如果使用的是Linux系统,可能需要安装它:
$ pip install python-tk一切安装完毕后,开始编写我们的计算器代码,在教程结束时,将搭建出类似下面的东西:
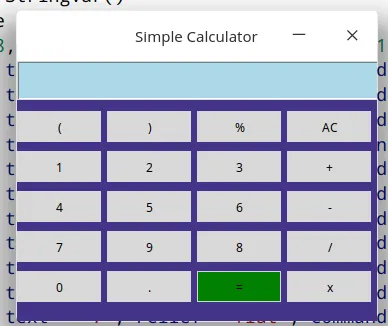 图片
图片
二、使用eval()解决数学问题
eval()是Python中的一个内置函数,它会解析表达式参数并将其作为Python表达式进行求值。
我们将使用eval()的概念来解决数学表达式。
用法示例:
>>> while True:
... expression = input('Enter equation: ')
... result = eval(expression)
... print(result)
...
Enter equation: 2 + (9/9) *3
5.0
Enter equation: 12 /9 + (18 -2) % 5
2.333333333333333使用这4行代码,已经在Python中制作了一个命令行计算器,现在让我们使用相同的概念来制作一个带有图形界面的计算器。
这个GUI计算器有三个主要部分:
- 用于显示表达式的屏幕(框架)
- 保存表达式值的按钮
- 搭建计算器逻辑
三、为计算器制作一个框架
from tkinter import Tk, Entry, Button, StringVar
class Calculator:
def __init__(self, master):
master.title('Simple Calculator')
master.geometry('360x260+0+0')
master.config(bg='#438')
master.resizable(False, False)
root = Tk()
calculator = Calculator(root)
root.mainloop()输出:
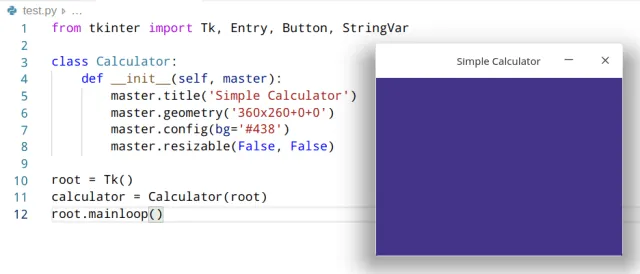 图片
图片
四、添加一个屏幕来显示表达式
from tkinter import Tk, Entry, Button, StringVar
class Calculator:
def __init__(self, master):
master.title('Simple Calculator')
master.geometry('360x260+0+0')
master.config(bg='#438')
master.resizable(False, False)
self.equation = StringVar()
self.entry_value = ''
Entry(width = 28,bg='lightblue', font = ('Times', 16), textvariable = self.equation).place(x=0,y=0)
root = Tk()
calculator = Calculator(root)
root.mainloop()输出:
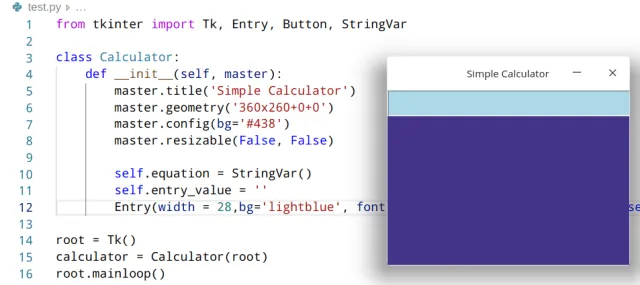 图片
图片
如上所示,我们已经完成了显示屏幕的构建,现在需要添加一个按钮用于形成数学表达式。
五、添加用于形成数学表达式的按钮
这些按钮的创建方式相同,只是它们所存储的值和它们的位置不同。用于形成数学表达式的按钮包括:
- 0到9的数字
- 数学运算符+、-、/、%
- 小数点
- 括号()
我们需要为每个按钮附加一个命令,以便当我们点击它时,它就会显示在显示屏上。为此,编写一个简单的show()函数来实现这个功能。
from tkinter import Tk, Entry, Button, StringVar
class Calculator:
def __init__(self, master):
master.title('Simple Calculator')
master.geometry('360x260+0+0')
master.config(bg='#438')
master.resizable(False, False)
self.equation = StringVar()
self.entry_value = ''
Entry(width = 28,bg='lightblue', font = ('Times', 16), textvariable = self.equation).place(x=0,y=0)
Button(width=8, text = '(', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('(')).place(x=0,y=50)
Button(width=8, text = ')', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(')')).place(x=90, y=50)
Button(width=8, text = '%', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('%')).place(x=180, y=50)
Button(width=8, text = '1', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(1)).place(x=0,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '2', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(2)).place(x=90,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '3', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(3)).place(x=180,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '4', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(4)).place(x=0,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '5', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(5)).place(x=90,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '6', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(6)).place(x=180,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '7', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(7)).place(x=0,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = '8', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(8)).place(x=180,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = '9', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(9)).place(x=90,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = '0', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(0)).place(x=0,y=210)
Button(width=8, text = '.', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('.')).place(x=90,y=210)
Button(width=8, text = '+', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('+')).place(x=270,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '-', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('-')).place(x=270,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '/', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('/')).place(x=270,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = 'x', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('*')).place(x=270,y=210)
def show(self, value):
self.entry_value +=str(value)
self.equation.set(self.entry_value)
root = Tk()
calculator = Calculator(root)
root.mainloop()输出:
输出是一个带有按钮的计算器,当你点击其中任意一个按钮时,它的值就会显示在显示屏上。
现在我们的计算器只剩下两个按钮就能完整,一个是重置按钮用于清除屏幕,另一个是等号(=)按钮,用于计算表达式并将结果显示在屏幕上。
六、为计算器添加重置和等号按钮
from tkinter import Tk, Entry, Button, StringVar
class Calculator:
def __init__(self, master):
master.title('Simple Calculator')
master.geometry('360x260+0+0')
master.config(bg='#438')
master.resizable(False, False)
self.equation = StringVar()
self.entry_value = ''
Entry(width = 28,bg='lightblue', font = ('Times', 16), textvariable = self.equation).place(x=0,y=0)
Button(width=8, text = '(', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('(')).place(x=0,y=50)
Button(width=8, text = ')', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(')')).place(x=90, y=50)
Button(width=8, text = '%', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('%')).place(x=180, y=50)
Button(width=8, text = '1', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(1)).place(x=0,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '2', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(2)).place(x=90,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '3', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(3)).place(x=180,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '4', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(4)).place(x=0,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '5', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(5)).place(x=90,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '6', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(6)).place(x=180,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '7', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(7)).place(x=0,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = '8', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(8)).place(x=180,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = '9', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(9)).place(x=90,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = '0', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(0)).place(x=0,y=210)
Button(width=8, text = '.', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('.')).place(x=90,y=210)
Button(width=8, text = '+', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('+')).place(x=270,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '-', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('-')).place(x=270,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '/', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('/')).place(x=270,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = 'x', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('*')).place(x=270,y=210)
Button(width=8, text = '=', bg='green', relief ='flat', command=self.solve).place(x=180, y=210)
Button(width=8, text = 'AC', relief ='flat', command=self.clear).place(x=270,y=50)
def show(self, value):
self.entry_value +=str(value)
self.equation.set(self.entry_value)
def clear(self):
self.entry_value = ''
self.equation.set(self.entry_value)
def solve(self):
result = eval(self.entry_value)
self.equation.set(result)
root = Tk()
calculator = Calculator(root)
root.mainloop()输出:
七、结语
在短短的五分钟内,我们成功地使用Tkinter库搭建了一个Python GUI计算器。这个计算器可以进行基本的数学运算,并为用户提供了友好的交互体验。
搭建一个GUI计算器不仅仅是一个有趣的项目,它还展示了Python的强大和灵活性。希望对你有所帮助,并激励你进一步探索和开发更多有趣的GUI应用程序!
相关内容
热门资讯
PHP新手之PHP入门
PHP是一种易于学习和使用的服务器端脚本语言。只需要很少的编程知识你就能使用PHP建立一个真正交互的...
网络中立的未来 网络中立性是什...
《牛津词典》中对“网络中立”的解释是“电信运营商应秉持的一种原则,即不考虑来源地提供所有内容和应用的...
各种千兆交换机的数据接口类型详...
千兆交换机有很多值得学习的地方,这里我们主要介绍各种千兆交换机的数据接口类型,作为局域网的主要连接设...
什么是大数据安全 什么是大数据...
在《为什么需要大数据安全分析》一文中,我们已经阐述了一个重要观点,即:安全要素信息呈现出大数据的特征...
如何允许远程连接到MySQL数...
[[277004]]【51CTO.com快译】默认情况下,MySQL服务器仅侦听来自localhos...
如何利用交换机和端口设置来管理...
在网络管理中,总是有些人让管理员头疼。下面我们就将介绍一下一个网管员利用交换机以及端口设置等来进行D...
P2P的自白|我不生产内容,我...
现在一提起P2P,人们就会联想到正在被有关部门“围剿”的互联网理财服务。×租宝事件使得劳...
Intel将Moblin社区控...
本周二,非营利机构Linux基金会宣布,他们将担负起Moblin社区的管理工作,而这之前,Mobli...
施耐德电气数据中心整体解决方案...
近日,全球能效管理专家施耐德电气正式启动大型体验活动“能效中国行——2012卡车巡展”,作为该活动的...
Windows恶意软件20年“...
在Windows的早期年代,病毒游走于系统之间,偶尔删除文件(但被删除的文件几乎都是可恢复的),并弹...