在Golang中理解错误处理
创始人
2025-07-05 00:21:28
0次
一、处理Golang中临时错误和最终错误的策略和示例
作为一名精通Golang的开发人员,您了解有效的错误处理是编写健壮可靠软件的关键因素。在复杂系统中,错误可能采取各种形式,包括临时故障和最终失败。在本文中,我们将探讨处理Golang中的临时错误和最终错误的最佳实践,并附有示例代码。

二、理解临时错误和最终错误
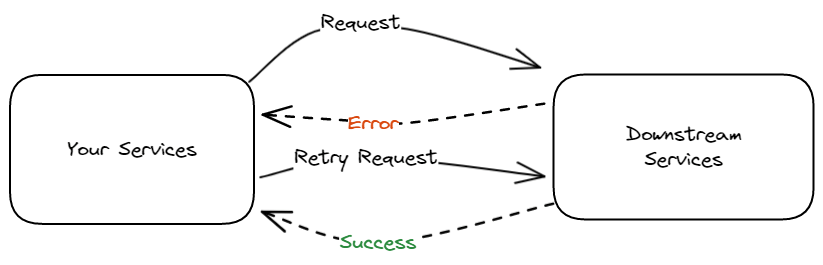
临时错误是瞬时问题,可能是由于短暂的网络中断、资源限制或其他非永久性因素引起的。这些错误通常可以通过在短暂延迟后重试操作来解决。另一方面,最终错误更严重,表明无论如何重试,操作都无法成功完成。
1.处理临时错误的优秀实践
- 重试机制: 为临时错误实施重试机制。这涉及捕获错误,等待一小段时间,然后再次尝试操作。
enter image description here
- 指数退避: 使用指数退避逐渐增加重试之间的延迟。这有助于防止通过重复请求而不断压倒系统,并为潜在的瞬时问题提供了解决的时间。
- 重试次数限制: 设置重试次数的限制,以防错误持续存在而导致无限循环。
- 上下文使用: 利用上下文包(context package)有效地管理重试和取消。这确保在必要时优雅地终止重试。
2.代码示例:处理临时错误
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net"
"time"
"context"
)
func fetchDataWithRetry(ctx context.Context) error {
retryCount := 0
maxRetries := 3
for {
// Simulate a temporary error
conn, err := net.Dial("tcp", "example.com:80")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Temporary error:", err)
if retryCount >= maxRetries {
return fmt.Errorf("max retries reached, giving up")
}
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
return ctx.Err()
case <-time.After(time.Duration(retryCount) * time.Second):
retryCount++
continue
}
}
// Successfully fetched data, process it
_ = conn.Close()
return nil
}
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
err := fetchDataWithRetry(ctx)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Final error:", err)
}
}在此示例中,fetchDataWithRetry 函数尝试使用指数退避来建立与服务器的连接,以处理临时错误。重试机制由上下文控制,如果达到最大重试次数,将返回最终错误。
3.处理最终错误的优秀实践
- 日志记录和警报: 详细记录最终错误以提供有意义的故障排除信息。实施警报机制以通知相关团队或个人。
- 优雅降级: 设计您的应用程序以在出现最终错误时优雅地降低功能。这可能涉及切换到备用机制或提供替代功能。
- 用户友好的消息: 在遇到最终错误时显示用户友好的错误消息。这有助于用户理解问题并采取适当的措施。
4.代码示例:处理最终错误
package main
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
)
func processUserData(userID int) error {
// Simulate a final error
if userID <= 0 {
return errors.New("invalid user ID")
}
// Process user data
fmt.Println("Processing user data for ID:", userID)
return nil
}
func main() {
userID := -1
err := processUserData(userID)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Final error:", err)
// Display user-friendly message or switch to fallback
}
}在此示例中,processUserData 函数在提供无效的用户ID时遇到最终错误。主函数通过记录错误来处理此错误,并可能显示用户友好的消息或切换到备用机制。
三、结论
有效的错误处理对于构建可靠的软件尤其重要,尤其是在像Golang这样的语言中。通过区分临时错误和最终错误,并应用适当的策略,您可以确保您的应用程序具有弹性且用户友好。借助本文中概述的最佳实践和附带的代码示例,您可以处理Golang项目中的临时故障和最终故障。请记住,良好构建的错误处理策略有助于整体稳定性和软件解决方案的成功。
相关内容
热门资讯
如何允许远程连接到MySQL数...
[[277004]]【51CTO.com快译】默认情况下,MySQL服务器仅侦听来自localhos...
如何利用交换机和端口设置来管理...
在网络管理中,总是有些人让管理员头疼。下面我们就将介绍一下一个网管员利用交换机以及端口设置等来进行D...
施耐德电气数据中心整体解决方案...
近日,全球能效管理专家施耐德电气正式启动大型体验活动“能效中国行——2012卡车巡展”,作为该活动的...
20个非常棒的扁平设计免费资源
Apple设备的平面图标PSD免费平板UI 平板UI套件24平图标Freen平板UI套件PSD径向平...
德国电信门户网站可实时显示全球...
德国电信周三推出一个门户网站,直观地实时提供其安装在全球各地的传感器网络检测到的网络攻击状况。该网站...
为啥国人偏爱 Mybatis,...
关于 SQL 和 ORM 的争论,永远都不会终止,我也一直在思考这个问题。昨天又跟群里的小伙伴进行...
《非诚勿扰》红人闫凤娇被曝厕所...
【51CTO.com 综合消息360安全专家提醒说,“闫凤娇”、“非诚勿扰”已经被黑客盯上成为了“木...
2012年第四季度互联网状况报...
[[71653]] 北京时间4月25日消息,据国外媒体报道,全球知名的云平台公司Akamai Te...