为什么创建 Redis 集群时会自动错开主从节点?
哈喽大家好,我是咸鱼。
在《一台服务器上部署 Redis 伪集群》这篇文章中,咸鱼在创建 Redis 集群时并没有明确指定哪个 Redis 实例将担任 master,哪个将担任 slave,然而 Redis 却自动完成了主从节点的分配工作。
如果大家在多台服务器部署过 Redis 集群的话,比如说在三台机器上部署三主三从的 redis 集群,你会观察到 Redis 自动地将主节点和从节点的部署位置错开。
举个例子:master 1 和 slave 3 在同一台机器上;master 2和 slave 1 在同一台机器上;master 3 和 slave 2 在同一台机器上,这是为什么呢?
我们知道老版本的 Redis 集群管理命令是 redis-trib.rb,新版本则换成了 redis-cli,这两个可执行文件其实是一个用 C 编写的脚本,小伙伴们如果看过这两个文件的源码就会发现原因就在下面这段代码里:
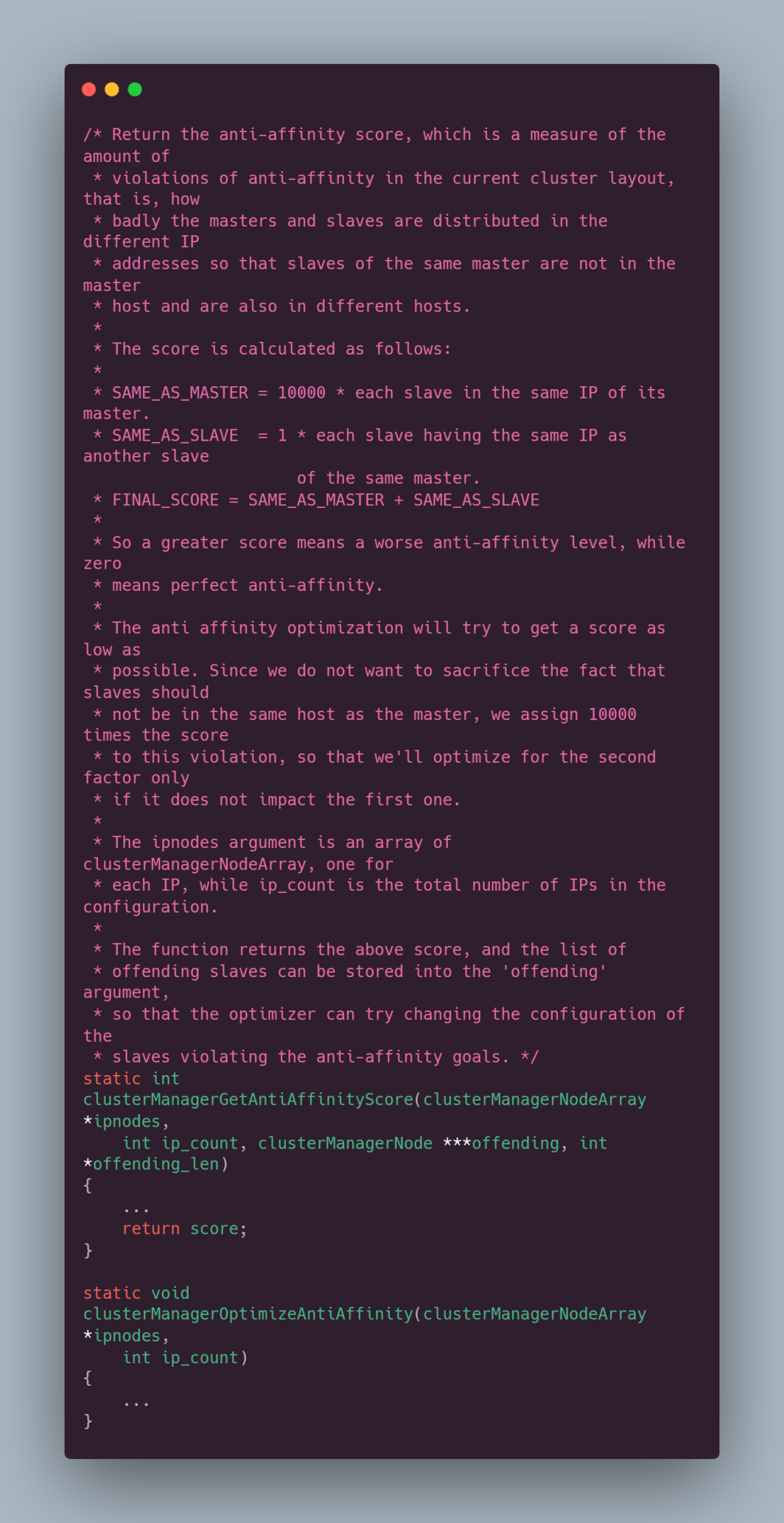
通过注释我们可以得知,clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore 函数是用来计算反亲和性得分,这个得分表示了当前 Redis 集群布局中是否符合反亲和性的要求,反亲和性指的是 master 和 slave 不应该在同一台机器上,也不应该在相同的 IP 地址上,那如何计算反亲和性得分呢?
- 如果有多个 slave 与同一个 master 在相同的 IP 地址上,那么对于每个这样的 slave,得分增加 10000
- 如果有多个 slave 在相同的 IP 地址上,但它们彼此之间不是同一个 master,那么对于每个这样的 slave,得分增加 1
- 最终得分是上述两部分得分之和。
也就是说,得分越高,亲和性越高;得分越低,反亲和性越高;得分为零表示完全符合反亲和性的要求。
获得得分之后,就会对得分高(反亲和性低)的节点进行优化。
为了让 Redis 主从之间的反亲和性更高,clusterManagerOptimizeAntiAffinity 函数会对那些反亲和性很低的节点进行优化,它会尝试通过交换从节点的主节点,来改善集群中主从节点分布,从而减少反亲和性低问题。
接下来我们分别来看下这两个函数:
反亲和性得分计算
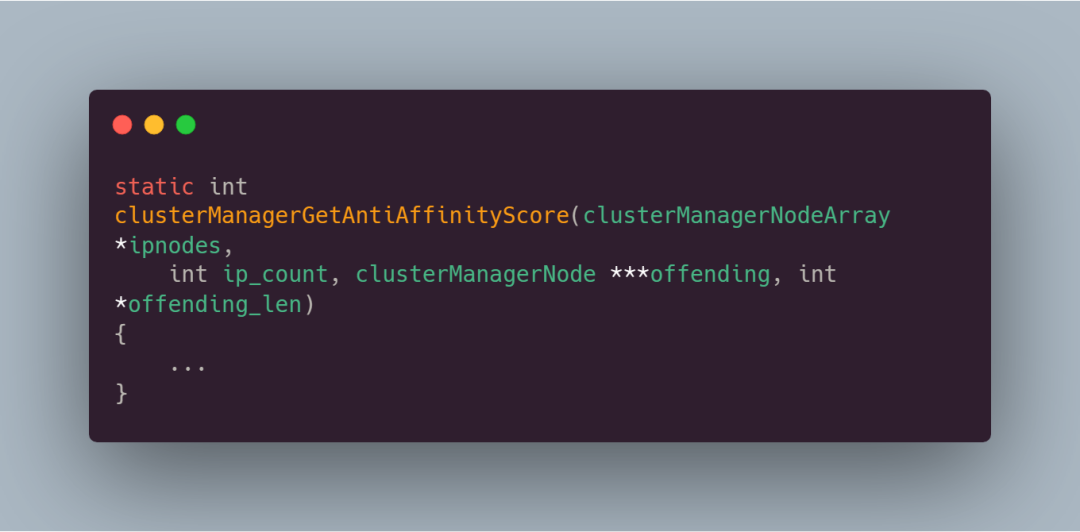
可以看到,该函数接受了四个参数:
- ipnodes:一个包含多个 clusterManagerNodeArray 结构体的数组,每个结构体表示一个 IP 地址上的节点数组
- ip_count:IP 地址的总数
- offending:用于存储违反反亲和性规则的节点的指针数组(可选参数)
- offending_len:存储 offending 数组中节点数量的指针(可选参数)
第一层 for 循环是遍历 ip 地址,第二层循环是遍历每个 IP 地址的节点数组:
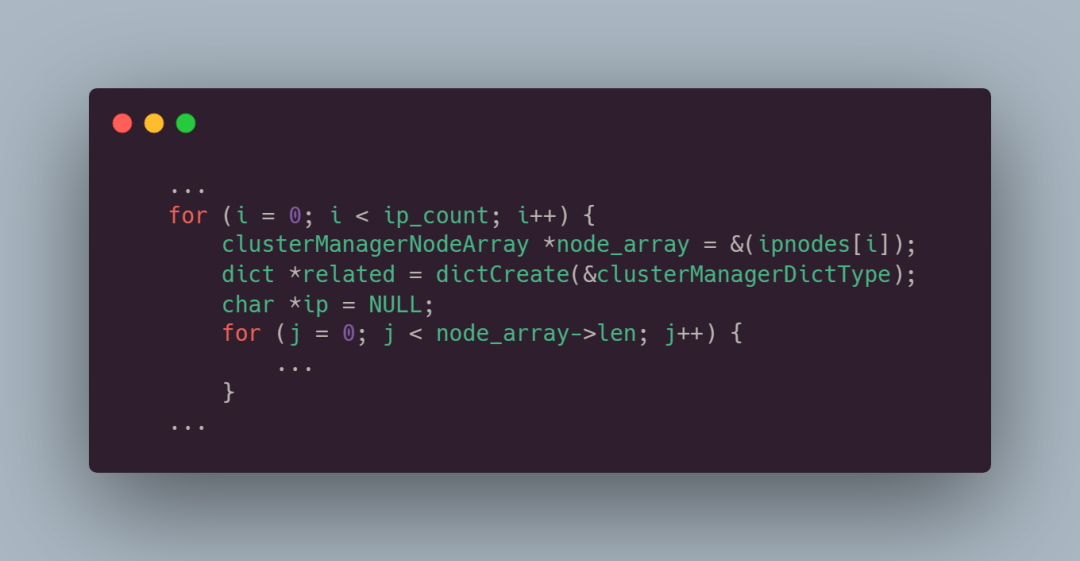
我们来看下第二层 for 循环:
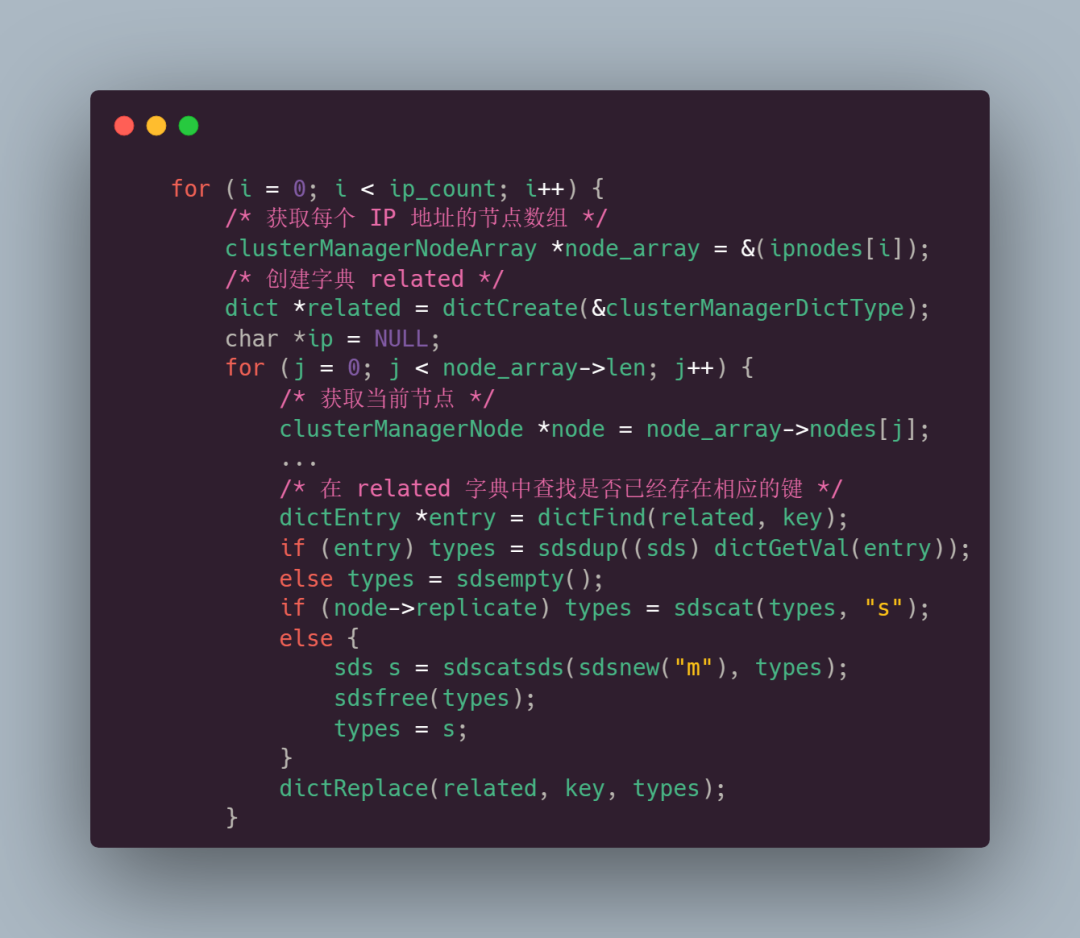
首先遍历每个 IP 地址的节点数组,对于每个 IP 地址上的节点数组,函数通过字典related来记录相同主节点和从节点的关系。
其中字典 related的 key 是节点的名称,value 是一个字符串,表示该节点类型 types,对于每个节点,根据节点构建一个字符串类型的关系标记(types),将主节点标记为 m,从节点标记为 s,然后通过字典将相同关系标记的节点关联在一起,构建了一个记录相同主从节点关系的字典 related:
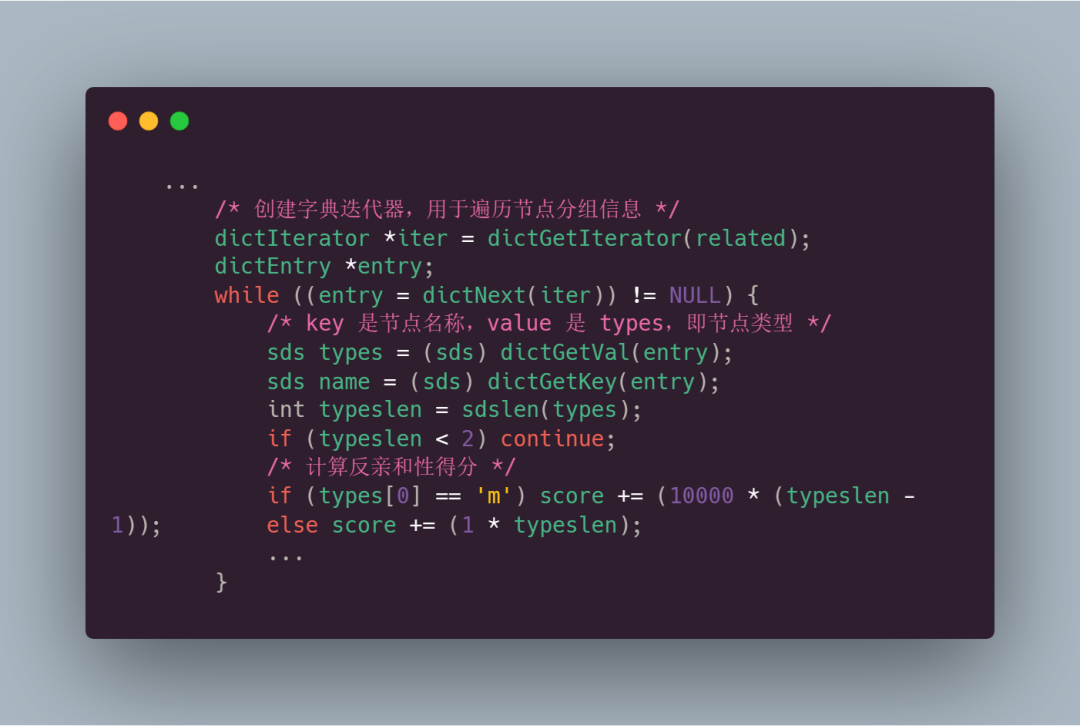
上面代码片段可知,while 循环遍历字典 related中的分组信息,计算相同主从节点关系的得分:
- 获取节点类型信息并长度
- 如果是主节点类型,得分 += (10000 * (typeslen - 1));否则,得分 += (1 * typeslen)
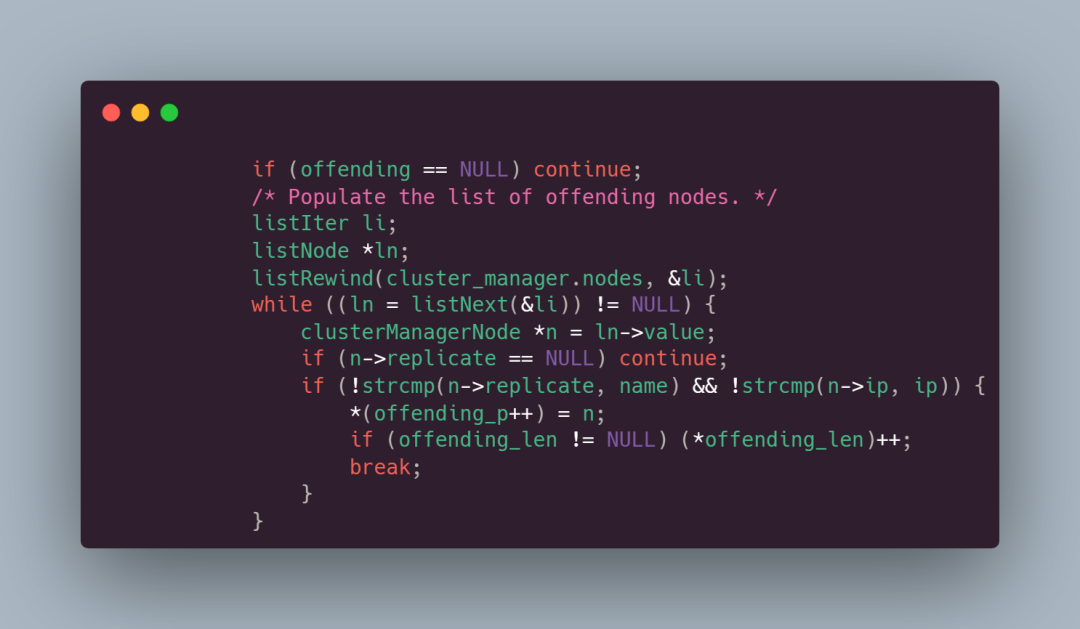
如果有提供 offending 参数,将找到违反反亲和性规则的节点并存储到 offending 数组中,同时更新违反规则节点的数量,如下代码所示:
最后返回得分 score,完整代码如下:
static int clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(clusterManagerNodeArray *ipnodes,
int ip_count, clusterManagerNode ***offending, int *offending_len)
{
int score = 0, i, j;
int node_len = cluster_manager.nodes->len;
clusterManagerNode **offending_p = NULL;
if (offending != NULL) {
*offending = zcalloc(node_len * sizeof(clusterManagerNode*));
offending_p = *offending;
}
/* For each set of nodes in the same host, split by
* related nodes (masters and slaves which are involved in
* replication of each other) */
for (i = 0; i < ip_count; i++) {
clusterManagerNodeArray *node_array = &(ipnodes[i]);
dict *related = dictCreate(&clusterManagerDictType);
char *ip = NULL;
for (j = 0; j < node_array->len; j++) {
clusterManagerNode *node = node_array->nodes[j];
if (node == NULL) continue;
if (!ip) ip = node->ip;
sds types;
/* We always use the Master ID as key. */
sds key = (!node->replicate ? node->name : node->replicate);
assert(key != NULL);
dictEntry *entry = dictFind(related, key);
if (entry) types = sdsdup((sds) dictGetVal(entry));
else types = sdsempty();
/* Master type 'm' is always set as the first character of the
* types string. */
if (node->replicate) types = sdscat(types, "s");
else {
sds s = sdscatsds(sdsnew("m"), types);
sdsfree(types);
types = s;
}
dictReplace(related, key, types);
}
/* Now it's trivial to check, for each related group having the
* same host, what is their local score. */
dictIterator *iter = dictGetIterator(related);
dictEntry *entry;
while ((entry = dictNext(iter)) != NULL) {
sds types = (sds) dictGetVal(entry);
sds name = (sds) dictGetKey(entry);
int typeslen = sdslen(types);
if (typeslen < 2) continue;
if (types[0] == 'm') score += (10000 * (typeslen - 1));
else score += (1 * typeslen);
if (offending == NULL) continue;
/* Populate the list of offending nodes. */
listIter li;
listNode *ln;
listRewind(cluster_manager.nodes, &li);
while ((ln = listNext(&li)) != NULL) {
clusterManagerNode *n = ln->value;
if (n->replicate == NULL) continue;
if (!strcmp(n->replicate, name) && !strcmp(n->ip, ip)) {
*(offending_p++) = n;
if (offending_len != NULL) (*offending_len)++;
break;
}
}
}
//if (offending_len != NULL) *offending_len = offending_p - *offending;
dictReleaseIterator(iter);
dictRelease(related);
}
return score;
}反亲和性优化
计算出反亲和性得分之后,对于那些得分很高的节点,redis 就需要对其进行优化,提高集群中节点的分布,以避免节点在同一主机上
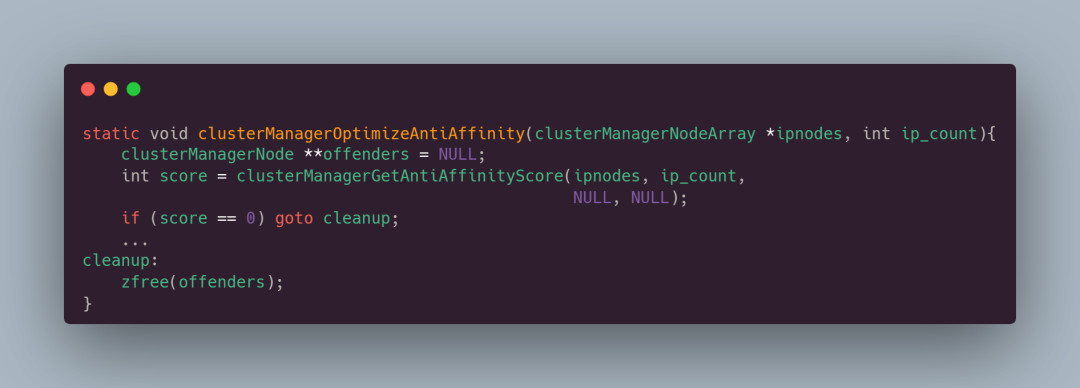
从上面的代码可以看到,如果得分为 0 ,说明反亲和性已经很好,无需优化。直接跳到 cleanup 去释放 offenders 节点的内存空间。
如果得分不为 0 ,则就会设置一个最大迭代次数maxiter,这个次数跟节点的数量成正比,然后 while 循环在有限次迭代内进行优化操作。

这个函数的核心就在 while 循环里,我们来看一下其中的一些片段:
首先 offending_len 来存储违反规则的节点数,然后如果之前有违反规则的节点(offenders != NULL)则释放掉(zfree(offenders));
然后重新计算得分,如果得分为0或没有违反规则的节点,退出 while 循环;
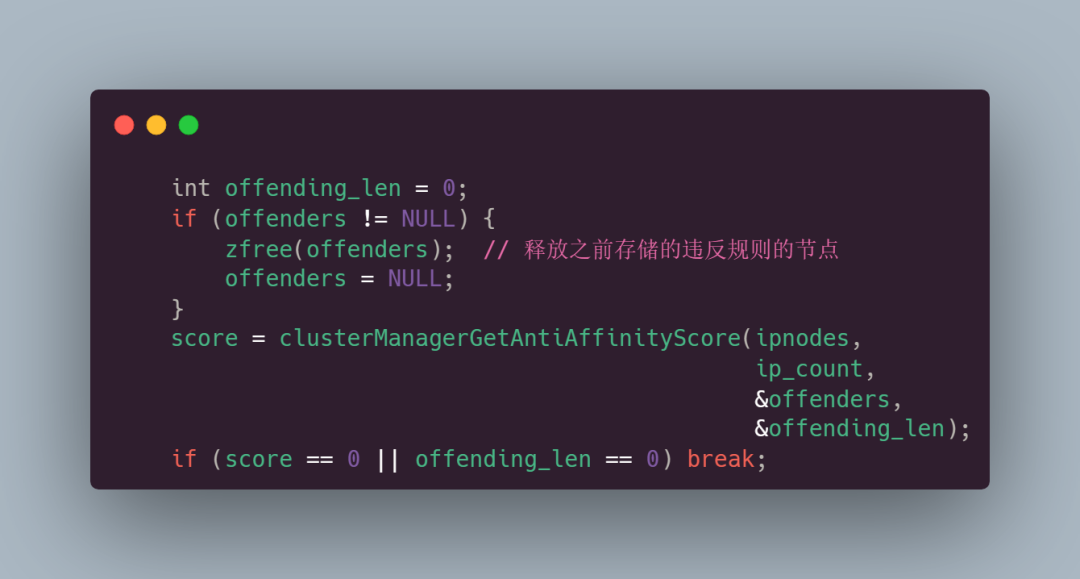
接着去随机选择一个违反规则的节点,尝试交换分配的 master:
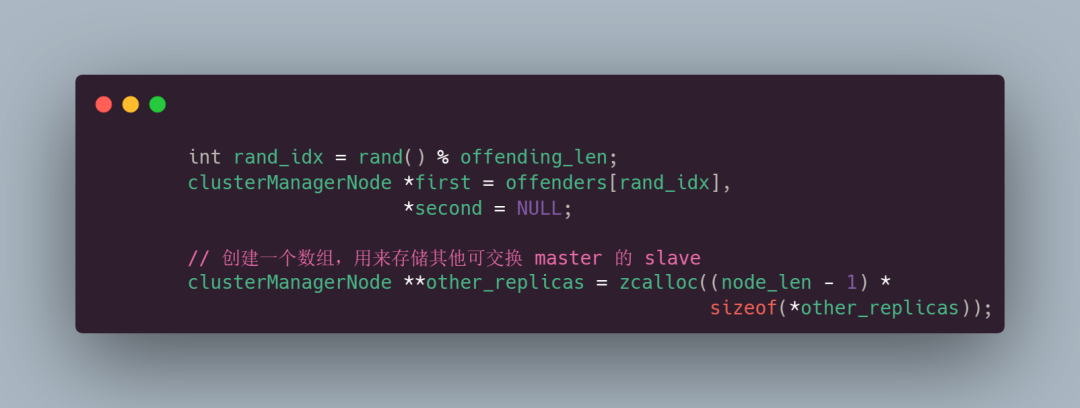
然后遍历集群中的节点,寻找能够交换 master 的 slave。如果没有找到,那就退出循环:
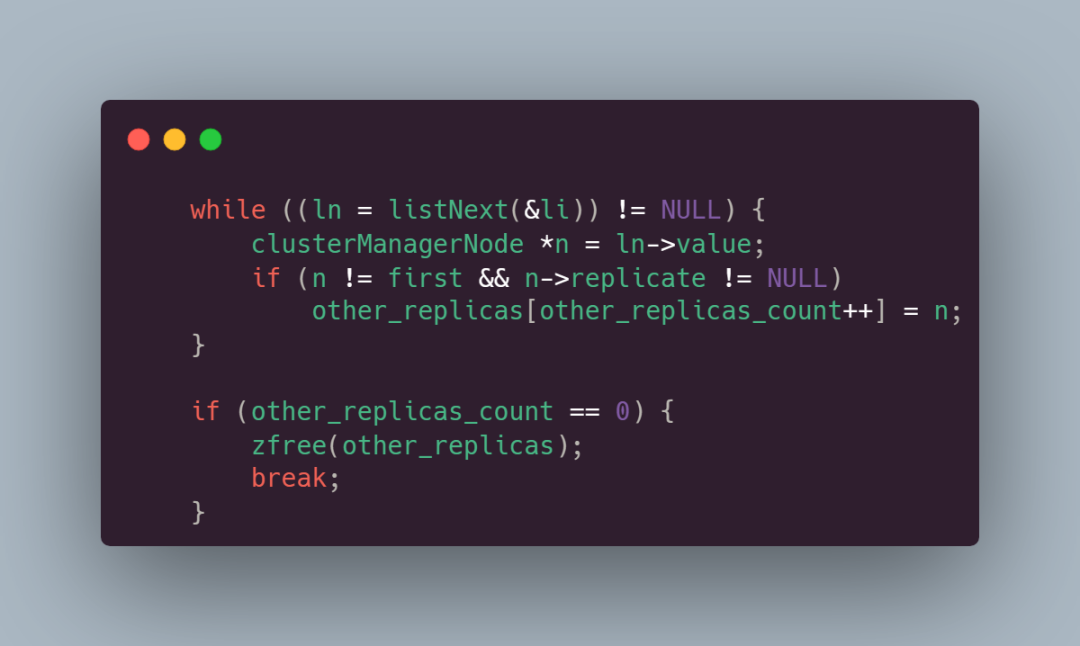
如果找到了,就开始交换并计算交换后的反亲和性得分:
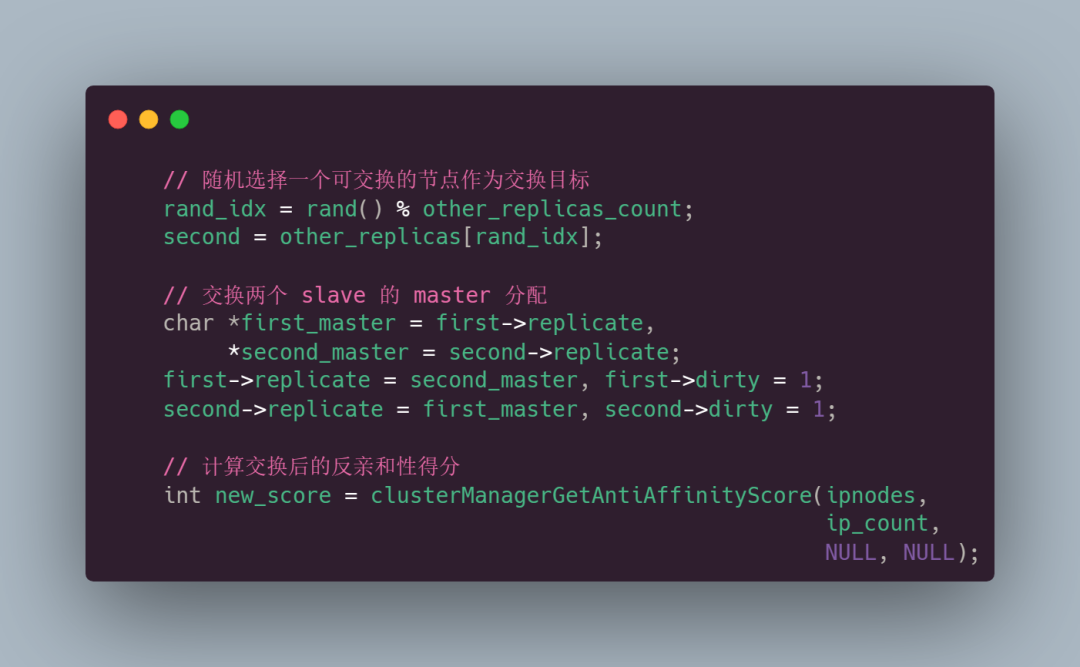
如果交换后的得分比之前的得分还大,说明白交换了,还不如不交换,就会回顾;如果交换后的得分比之前的得分小,说明交换是没毛病的:
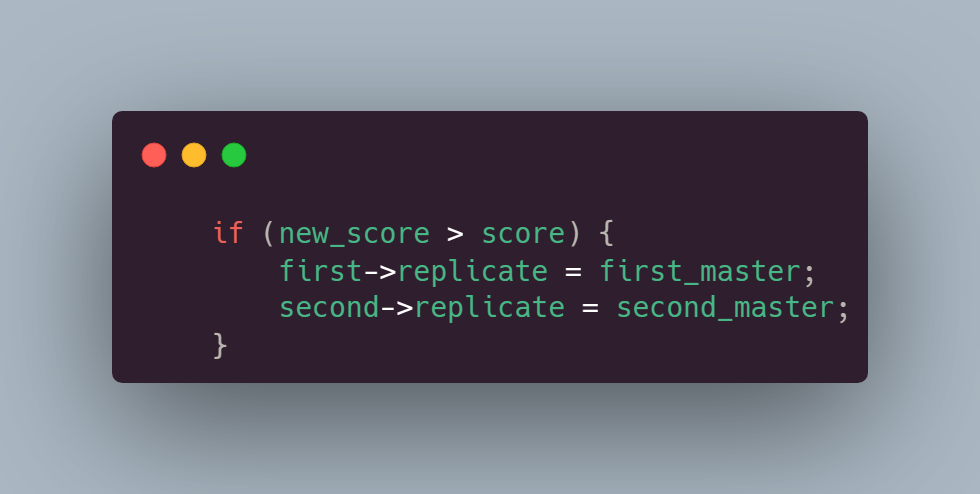
最后释放资源,准备下一次 while 循环:

总结一下:
- 每次 while 循环会尝试随机选择一个违反反亲和性规则的从节点,并与另一个随机选中的从节点交换其主节点分配,然后重新计算交换后的反亲和性得分
- 如果交换后的得分变大,说明交换不利于反亲和性,会回滚交换
- 如果交换后得分变小,则保持,后面可能还需要多次交换
- 这样,通过多次随机的交换尝试,最终可以达到更好的反亲和性分布
最后则是一些收尾工作,像输出日志信息,释放内存等,这里不过多介绍:
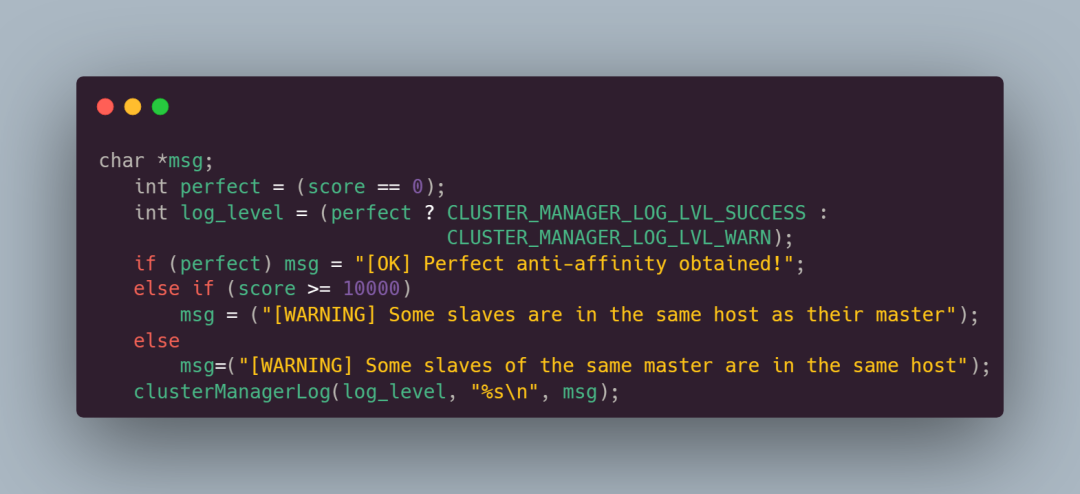
下面是完整代码:
static void clusterManagerOptimizeAntiAffinity(clusterManagerNodeArray *ipnodes,
int ip_count)
{
clusterManagerNode **offenders = NULL;
int score = clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(ipnodes, ip_count,
NULL, NULL);
if (score == 0) goto cleanup;
clusterManagerLogInfo(">>> Trying to optimize slaves allocation "
"for anti-affinity\n");
int node_len = cluster_manager.nodes->len;
int maxiter = 500 * node_len; // Effort is proportional to cluster size...
srand(time(NULL));
while (maxiter > 0) {
int offending_len = 0;
if (offenders != NULL) {
zfree(offenders);
offenders = NULL;
}
score = clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(ipnodes,
ip_count,
&offenders,
&offending_len);
if (score == 0 || offending_len == 0) break; // Optimal anti affinity reached
/* We'll try to randomly swap a slave's assigned master causing
* an affinity problem with another random slave, to see if we
* can improve the affinity. */
int rand_idx = rand() % offending_len;
clusterManagerNode *first = offenders[rand_idx],
*second = NULL;
clusterManagerNode **other_replicas = zcalloc((node_len - 1) *
sizeof(*other_replicas));
int other_replicas_count = 0;
listIter li;
listNode *ln;
listRewind(cluster_manager.nodes, &li);
while ((ln = listNext(&li)) != NULL) {
clusterManagerNode *n = ln->value;
if (n != first && n->replicate != NULL)
other_replicas[other_replicas_count++] = n;
}
if (other_replicas_count == 0) {
zfree(other_replicas);
break;
}
rand_idx = rand() % other_replicas_count;
second = other_replicas[rand_idx];
char *first_master = first->replicate,
*second_master = second->replicate;
first->replicate = second_master, first->dirty = 1;
second->replicate = first_master, second->dirty = 1;
int new_score = clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(ipnodes,
ip_count,
NULL, NULL);
/* If the change actually makes thing worse, revert. Otherwise
* leave as it is because the best solution may need a few
* combined swaps. */
if (new_score > score) {
first->replicate = first_master;
second->replicate = second_master;
}
zfree(other_replicas);
maxiter--;
}
score = clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(ipnodes, ip_count, NULL, NULL);
char *msg;
int perfect = (score == 0);
int log_level = (perfect ? CLUSTER_MANAGER_LOG_LVL_SUCCESS :
CLUSTER_MANAGER_LOG_LVL_WARN);
if (perfect) msg = "[OK] Perfect anti-affinity obtained!";
else if (score >= 10000)
msg = ("[WARNING] Some slaves are in the same host as their master");
else
msg=("[WARNING] Some slaves of the same master are in the same host");
clusterManagerLog(log_level, "%s\n", msg);
cleanup:
zfree(offenders);
}