CCIE ISP-Inter-AS MPLS solutions - Back-to-Back vrf’s
When configuring inter-as mpls vpn’s you’ve got 3 options to choose from.
A - Back-to-Back VRF’s
B - MP-eBGP for VPNv4
C - Multi-hop EBGP VPNv4
This post is about option A. I will show how to configure inter-as vpn’s using back-to-back vrf’s. Below you can see the diagram used for the purpose of this post.
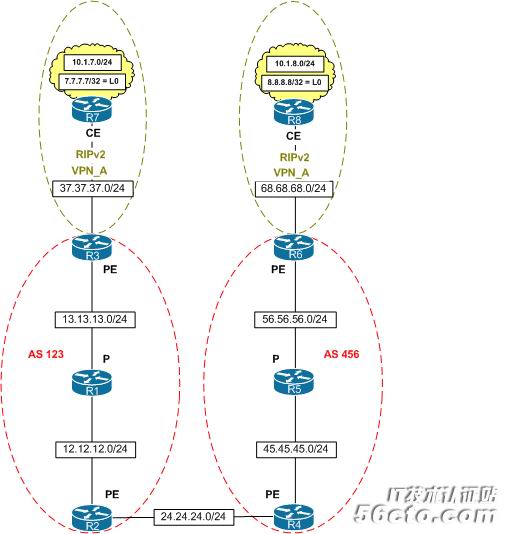 |
With back-to-back vrf’s what you’ll do is basically make the connected PE’s think of each other as CE’s. You can run any supported PE-CE routing protocol over the per VPN logical interface between the directly connected ASBR’s. This option is seen as the easiest one to configure, a drawback is that this option doesn’t scale very well as the numbers of VPN’s start to grow.
Below the working configurations for this inter-as solution, I left out the configurations for router R1, R5, R7 and R8 because there is nothing special configured on these routers (they’re just simple P-routers and CE routers running RIPv2).
R2 :
hostname R2 ! ip cef ! ip vrf VPN_A rd 2.2.2.2:1 route-target export 2.2.2.2:1 route-target import 3.3.3.3:1 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ! interface Loopback1 ip vrf forwarding VPN_A ip address 22.22.22.22 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip vrf forwarding VPN_A ip address 24.24.24.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 12.12.12.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto tag-switching ip ! router ospf 100 vrf VPN_A log-adjacency-changes redistribute bgp 123 subnets network 22.22.22.22 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 24.24.24.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! router ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 log-adjacency-changes network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 12.12.12.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! router bgp 123 bgp router-id 2.2.2.2 no bgp default ipv4-unicast bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 123 neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf VPN_A redistribute ospf 100 vrf VPN_A match internal external 1 external 2 no auto-summary no synchronization exit-address-family |
R4 :
hostname R4 ! ip cef ! ip vrf VPN_A rd 4.4.4.4:1 route-target export 4.4.4.4:1 route-target import 6.6.6.6:1 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 ! interface Loopback1 ip vrf forwarding VPN_A ip address 44.44.44.44 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip vrf forwarding VPN_A ip address 24.24.24.4 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 45.45.45.4 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto tag-switching ip ! router ospf 100 vrf VPN_A log-adjacency-changes redistribute bgp 456 subnets network 24.24.24.4 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 44.44.44.44 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! router ospf 1 router-id 4.4.4.4 log-adjacency-changes network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 45.45.45.4 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! router bgp 456 bgp router-id 4.4.4.4 no bgp default ipv4-unicast bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 6.6.6.6 remote-as 456 neighbor 6.6.6.6 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 6.6.6.6 activate neighbor 6.6.6.6 send-community both exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf VPN_A redistribute ospf 100 vrf VPN_A match internal external 1 external 2 no auto-summary no synchronization exit-address-family |
#p3
R3 :
hostname R3 ! ip cef ! ip vrf VPN_A rd 3.3.3.3:1 route-target export 3.3.3.3:1 route-target import 2.2.2.2:1 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 no ip address duplex auto speed auto ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 13.13.13.3 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto tag-switching ip ! interface FastEthernet2/0 ip vrf forwarding VPN_A ip address 37.37.37.3 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! router ospf 1 router-id 3.3.3.3 log-adjacency-changes network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 13.13.13.3 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! router rip version 2 no auto-summary ! address-family ipv4 vrf VPN_A redistribute bgp 123 metric transparent network 37.0.0.0 no auto-summary exit-address-family ! router bgp 123 bgp router-id 3.3.3.3 no bgp default ipv4-unicast bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 123 neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf VPN_A redistribute rip no auto-summary no synchronization exit-address-family |
R6 :
hostname R6 ! ip cef ! ip vrf VPN_A rd 6.6.6.6:1 route-target export 6.6.6.6:1 route-target import 4.4.4.4:1 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip vrf forwarding VPN_A ip address 61.61.61.6 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 56.56.56.6 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto tag-switching ip ! interface FastEthernet2/0 ip vrf forwarding VPN_A ip address 68.68.68.6 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! router ospf 1 router-id 6.6.6.6 log-adjacency-changes network 6.6.6.6 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 56.56.56.6 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! router rip version 2 no auto-summary ! address-family ipv4 vrf VPN_A redistribute bgp 456 metric transparent network 68.0.0.0 no auto-summary exit-address-family ! router bgp 456 bgp router-id 6.6.6.6 no bgp default ipv4-unicast bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 456 neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate neighbor 4.4.4.4 send-community both exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf VPN_A redistribute rip no auto-summary no synchronization exit-address-family |
As you can see we run a separate instance of the OSPF process between router R2 and R4, under this process we redistribute BGP.
Now let’s do a “show ip route” on router R7 :
R7 :
R7#sh ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
68.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
R 68.68.68.0 [120/2] via 37.37.37.3, 00:00:07, FastEthernet1/3
37.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 37.37.37.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/3
22.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
R 22.22.22.22 [120/1] via 37.37.37.3, 00:00:07, FastEthernet1/3
7.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 7.7.7.7 is directly connected, Loopback0
8.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
R 8.8.8.8 [120/2] via 37.37.37.3, 00:00:07, FastEthernet1/3
24.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
R 24.24.24.0 [120/1] via 37.37.37.3, 00:00:07, FastEthernet1/3
44.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
R 44.44.44.44 [120/3] via 37.37.37.3, 00:00:09, FastEthernet1/3
|
As you can see router R7 can see router R8
【编辑推荐】
- CCIE Lab考试可以放心使用"show run"命令
- CCIE找工作指南
- 思科今年各CCIE考试形势分析读后感